
In November 2022, the Guangzhou Arbitration Commission (GZAC) reported on its social media platform that the Metaverse Arbitration Court it set up had recently awarded the first case involving the virtviual world.
The case involved the creation of virtual avatars in the Metaverse community and the trading of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFT). After acquiring the digital image from an NFT development company, the party applied it to offline clothing printing and planned to sell related clothes. This behavior led to a copyright dispute brought before the arbitration institution.
According to the arbitration agreement reached by mutual consent, the parties referred their disputes to the Meta City (Yuanbang) Arbitration Court (元邦仲裁院) through the Metaverse e-filing channel of the GZAC.
Ultimately, in the presence of arbitrators, the NFT company granted the other party the right to use the digital image, and would share the profit when the other party used it.
This case fulfilled its arbitration process in the Metaverse. For more about the Metaverse arbitration tribunal scene, please see the picture below:
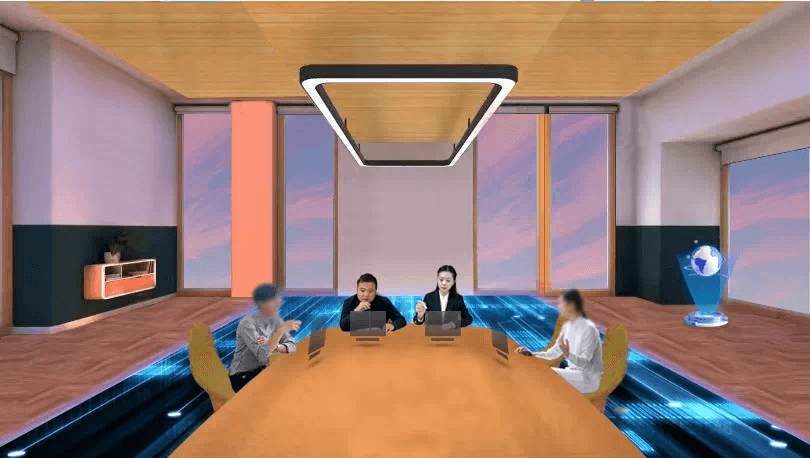

The GZAC stated that it set up the first Metaverse arbitration court, Meta City (Yuanbang) Arbitration Court, in July 2022. It is located in the main building of Meta City Hall, the Scales Floating Island, making it the first Metaverse arbitration court worldwide.
The picture below shows where this court is located in the Metaverse.
Cover Photo by Qingbao Meng on Unsplash
Contributors: CJO Staff Contributors Team








